Directory Browsing
Directory browsing, sometimes also referred as "directory listing" happens when a web server shows a public list of files and folders kept in a directory of a website, instead of fetching a webpage when that specific URL is requested in a visitor's browser.
- If directory browsing is enabled, anyone can visit URLs like /images/ or /uploads/ and see what files are stored in that folder.
- This can expose sensitive files and reveal your website's server structure to attackers.
- Disabling directory listing is a common baseline security best practice for most websites.
What is Directory Browsing?
Directory browsing is a server behavior where requesting a folder path displays an automatically generated “index” of the content of that folder.
Here is how it looks on a web browser, when directory browsing is enabled on a website
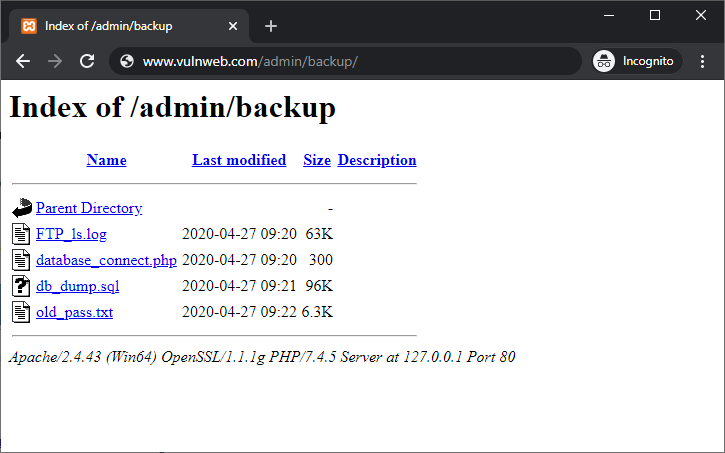
Example: If someone visits https://example.com/back-up/ and there’s no index.html, index.php or another default HTML document present - then the web server may show the entire content of the folder to the user in the web browser. The content of the folder would usually start with a heading - "index of /path-of-folder", below which all the files and folders residing in that folder will be shown to the user.
Even if you never intended to show the files and folders publicly, they are still discoverable beacause directory listing is enabled on the web server and has not been disabled. On the other hand, if the website shows 403 Forbidden or loads a proper page, directory browsing is likely disabled from the web server.
In addition to revealing the files and folders of a website, directory listing may also allow people to download your files through clickable links. Users can see file sizes and the last modified date, as depicted in the above image.
Why Directory Browsing is a Security Risk
Directory listings can create real problems even if the files seem harmless. It's like you have left a gate open, and anyone can enter your office and find out where everything is, and get a download of your files and folders, and later use that information against you.
Given below are the top reasons why directory browsing or directory listing is considered a significant security risk for websites
- Exposure of your website's file structure - Directory browsing exposes the directory structure of your website and allows anyone to browse through different directories. In some situations, visitors may see the content of important folders such as - backups, logs, exports - which is definitely a significant security risk.
- Easier attacks - attackers can quickly discover upload folders, scripts, or outdated assets. It just makes launching website attacks so much easier because now attackers have access to "Information".
- Unintended downloads - private documents or temporary files becomes publicly accessible.
- Compliance and privacy risk - accidental exposure of sensitive data may create legal or regulatory trouble.
Do’s and Don’ts
Do’s
- Disable directory listing - Disable Directory browsing site wide, unless you have a very specific reason not to.
- Allow browsing only when intended - If absolutely requiredm, enable it only on a dedicated directory only.
- Add index.html files in empty directories - Even a blank index.html can prevent directory listings on many servers.
- Re-test after migrations - Server moves, CDN changes, and configuration updates can accidentally re enable directory listing.
Don’ts
- Don’t assume no one will find it - People can guess folder links and check what’s inside, if directory browsing is enabled.
- Don't keep sensitive files in public directories - Don’t store backups, logs, or exports inside web accessible folders. You never know when and how things will go wrong at some point.
- Don’t forget subdomains and staging: - Check subdomains and staging environments as well, not just your main production environment.
FAQs on CSS Compression
Not exactly. A file can be accessible if someone knows the exact URL. Directory browsing makes discovery easy by listing everything - including the ones that you do not intend to share with anyone.
For most websites, yes. For a controlled public download directory, it can be acceptable if intentionally configured and secured through other configurations.
Yes. If directory listing is public, search engines can crawl and index the directory URL and sometimes the individual files.
Not always, but it is considered a good practice to let the browser render only one final CSS file, when compared to rendering multiple CSS files. The main goal is to reduce total bytes, avoid duplication, and ensure CSS is cached well. Combining CSS files into one can help in most setups but isn’t mandatory.
You should disable directory listing for that folder , or better, disable directory listing for the entire website.Next, you should remove any sensitive files from public paths, and re-check other common directories (uploads, backups, old folders).
Yes. Most web servers show a directory listing only when a folder has no default “index” file. Adding an index.html can prevent listings, but server level settings are the better long term fix.
Both techniques are okay but the standard practice is to return a 403 status code and not re-direct users automatically. The key thing to note is not to expose the file list and the directory structure of your website.
